What is DOM?
For accessing and manipulating documents, a standard is defined by the DOM.
“The W3C Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform and language-neutral interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a document.”
For accessing and manipulating HTML documents, the HTML DOM defines a standard way and presents an HTML document as a tree-structure. For accessing and manipulating XML documents, the XML DOM defines a standard way and presents an XML document as a tree-structure. For working with HTML or XML, a good understanding of DOM is necessary.
The HTML DOM:
Through the HTML DOM, we can access all the HTML elements.
Example:
Hello World!!
How are you?
Output:

Explanation:
In the above example, the value of an HTML element changes with id=”100″, i.e., the first <h1> element in the HTML document.
Example:
Hello World!!
Hello
How are you?
Output:
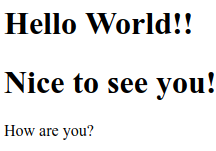
Explanation:
In the above example, we are using the getElementsByTagName() method which always returns an array. Thus, we will have to specify the array index [1], even if the HTML document contains a single <h1> element.
The XML DOM:
The way to get, change, add, and delete XML elements is defined by the XML DOM as a standard. Through the XML DOM, we can access all the XML elements. It is a standard object model and a standard programming interface for XML. It is platform- and language-independent and is a W3C standard.
Get the Value of an XML Element:
To get the text value of the first <title> element in an XML document, use the below code.
Example:
txt = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("title")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
Loading an XML File:
Books.xml:
ABC
Author Name
2020
100.00
XQuery Book
Author 1
Author 2
Author 3
Author 4
2004
350.00
Example:
Output:
XQuery Book
Explanation:
In the above example, we are reading “books.xml” into xmlDoc. The text value of the first <title> element in books.xml is then retrieved.
- xmlDoc: Used to define the XML DOM object created by the parser.
- getElementsByTagName(“title”)[0]: Used to get the first <title> element.
- childNodes[0]: Used to get the first child of the <title> element (the text node)
- nodeValue: Used to get the value of the node (the text itself).
Loading an XML String:
This example loads a text string into an XML DOM object, and extracts the info from it with JavaScript:
Example:
Output:

Explanation:
In the above example, we are loading a text string into an XML DOM object. We then extract the info from it with JavaScript.
Programming Interface:
XML is modeled as a set of node objects by DOM. To access the nodes we can use JavaScript or other programming languages. Here, we are using JavaScript. A set of standard properties and methods defines the programming interface to the DOM.
XML DOM Properties:
Some typical DOM properties are listed below. Here, x is a node object.
- x.nodeName: The name of x.
- x.nodeValue: The value of x.
- x.parentNode: The parent node of x.
- x.childNodes: The child nodes of x.
- x.attributes: The attributes nodes of x.
XML DOM Methods:
Some typical DOM methods are listed below. Here, x is a node object.
- x.getElementsByTagName(name): Used to get all elements with a specified tag name.
- x.appendChild(node): Used to insert a child node to x.
- x.removeChild(node): Used to remove a child node from x.